PawSQL for OceanBase Database
OceanBase database has been widely adopted in finance, e-commerce, and government sectors due to its high availability, strong consistency, and high performance. As business scale expands and data volume surges, optimizing OceanBase database query performance becomes increasingly important. PawSQL provides comprehensive performance optimization support for OceanBase database, helping users fully unleash OceanBase's performance potential.
I. Core Optimization Technologies
PawSQL introduces two specialized capabilities for OceanBase database:
1. Deep OceanBase SQL Syntax Support
- Dual-mode compatibility: Full support for MySQL/Oracle syntax systems
- Complete parsing of OceanBase-specific DDL syntax:
CREATE TABLE nation_d (
n_nationkey INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
n_name CHAR(25) NOT NULL,
n_regionkey INTEGER NOT NULL,
n_comment VARCHAR(152)
) duplicate_scope = cluster/none;
CREATE TABLE part (
p_partkey int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
p_name VARCHAR(55) NOT NULL,
p_mfgr CHAR(25) NOT NULL,
p_brand CHAR(10) NOT NULL,
p_type VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
p_size NUMBER NOT NULL,
p_container CHAR(10) NOT NULL,
p_retailprice NUMBER(15,2) NOT NULL,
p_comment VARCHAR(23)
) PARTITION BY HASH(p_partkey) PARTITIONS 16;
2. Rule System Upgrade
- Three new distributed design standards:
- Avoid table join fields that are not distribution keys
- DML in distributed databases should avoid table joins
- DML operations in distributed databases lack sharding field equality conditions
- Three new distribution key design standards:
- Local tables are not recommended in distributed databases
- Multiple fields are not recommended for distribution keys
- Distribution keys should use highly distinctive fields
- Two new distribution strategy design standards:
- Replicated distribution is not recommended for large tables
- Hash distribution is recommended for distribution method
II. Product Matrix of SQL Lifecycle
2.1 Development and Testing Phase: Intelligent SQL Optimization
PawSQL Optimization Platform is a one-stop online SQL optimization tool for application developers and testers. It integrates industry best practices for relational database query optimization, helping application developers and database administrators solve SQL performance issues through query rewriting optimization and intelligent index recommendations. PawSQL Optimization Platform has completed integration with common IDEs, allowing developers to perform SQL optimization without leaving their development environment.
The PawSQL Optimization Platform is an online SQL optimization tool for developers and DBAs, incorporating industry-leading query optimization technologies, including:
- Intelligent Query Rewriting: Automatically optimizes inefficient SQL statements
- Index Recommendation Engine: Precisely recommends optimal index combinations
- Distributed Optimization Strategies: Provides specialized optimization suggestions for OceanBase's distributed characteristics
2.2 Integration Phase: Intelligent SQL Review
PawSQL Review Platform, with its leading core technologies such as self-developed SQL parser, syntax tree-based rule matching, and context information updates, provides comprehensive and precise (accuracy over 95%) intelligent SQL review capabilities for SQL quality management teams. It conducts comprehensive checks from multiple dimensions including syntax specifications, performance efficiency, and security, providing targeted optimization suggestions to help enterprises improve SQL performance and application efficiency.
For OceanBase database's distributed characteristics, PawSQL provides specialized distributed query optimization suggestions, with applicable rules exceeding 190.
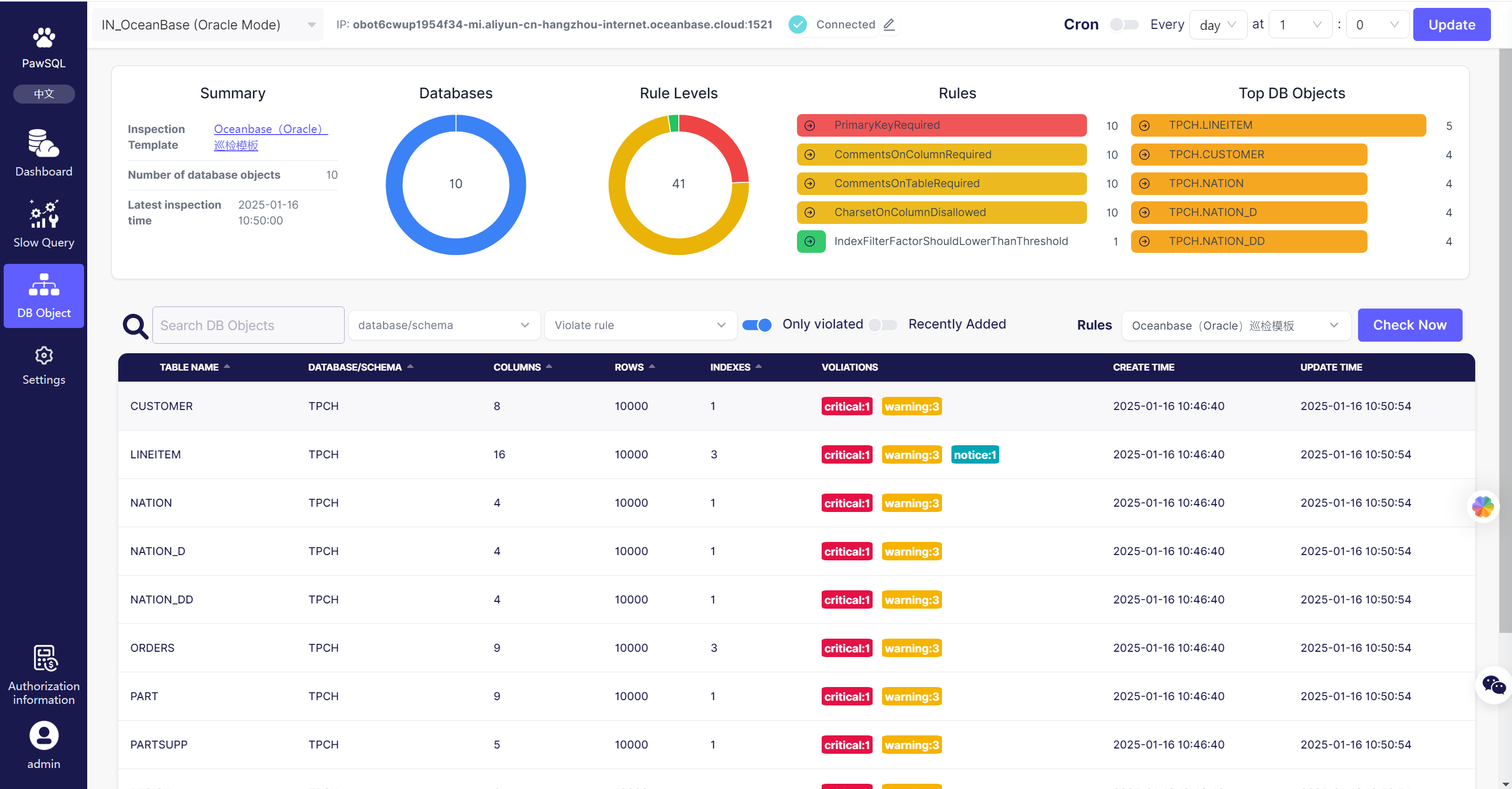
2.3 Operating Phase: Performance Patroller
PawSQL Database Performance Patroller automatically captures slow queries generated in the database periodically and provides SQL optimization suggestions, including automatic SQL rewriting, intelligent index recommendations, and existing redundant index analysis. It automatically inspects database objects periodically, identifying potential performance, security, and maintainability issues, and provides optimization suggestions.
III. Summary
PawSQL for OceanBase database provides you with a one-stop performance optimization solution. From daily query optimization to complex distributed scenario handling, PawSQL can help you tackle challenges with ease. 🚀 Experience PawSQL now and unlock OceanBase database's performance potential!